
|
|
|
|
OPC 10000-19 |
|
|
OPC Unified Architecture Part 19: Dictionary Reference
Release 1.05.03 2023-12-31
|

|
|
|
|
OPC 10000-19 |
|
|
OPC Unified Architecture Part 19: Dictionary Reference
Release 1.05.03 2023-12-31
|

|
Specification Type: |
Industry Standard Specification |
Comments: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Document |
OPC 10000-19 |
|
|
|
Title: |
OPC Unified Architecture |
Date: |
2023-12-31 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Version: |
Release 1.05.03 |
Software: |
MS-Word |
|
|
|
Source: |
OPC 10000-19 - UA Specification Part 19 - Dictionary Reference 1.05.03.docx |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Author: |
OPC Foundation |
Status: |
Release |
|
|
|
|
|
CONTENTS
Page
3 Terms, definitions, abbreviated terms, and conventions
4 Dictionary Reference Information Model overview
5.3 IRDI ISO/IEC 11179-6 conformant DictionaryEntryType
5.4 URI based dictionary entry type
6.1 HasDictionaryEntry ReferenceType
7.1 MultiStateDictionaryEntryDiscreteBaseType VariableType
7.2 MultiStateDictionaryEntryDiscreteType VariableType
Figures
Figure 1 – The dictionary reference types................................................................. 3
Figure 2 – IRDI overview....................................................................................... 4
Figure 3 – DeviceType Property example.................................................................. 7
Figure 4 – Example with references to classes and properties........................................ 8
Figure 5 – Example with two dictionaries.................................................................. 9
Tables
Table 1 – DictionaryEntryType definition
Table 2 – DictionaryFolderType definition
Table 3 – IrdiDictionaryEntryType Definition
Table 4 – UriDictionaryEntryType Definition
Table 5 – HasDictionaryEntry ReferenceType
Table 6 – MultiStateDictionaryEntryDiscreteBaseType Definition
Table 7 – MultiStateDictionaryEntryDiscreteType Definition
Table 8 – Dictionaries Definition
OPC Foundation
____________
UNIFIED ARCHITECTURE
This specification is the specification for developers of OPC UA applications. The specification is a result of an analysis and design process to develop a standard interface to facilitate the development of applications by multiple vendors that shall inter-operate seamlessly together.
Copyright © 2006-2023, OPC Foundation, Inc.
COPYRIGHT RESTRICTIONS
Any unauthorized use of this specification may violate copyright laws, trademark laws, and communications regulations and statutes. This document contains information which is protected by copyright. All Rights Reserved. No part of this work covered by copyright herein may be reproduced or used in any form or by any means--graphic, electronic, or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, taping, or information storage and retrieval systems--without permission of the copyright owner.
OPC Foundation members and non-members are prohibited
from copying and redistributing this specification. All copies must be obtained
on an individual basis, directly from the OPC Foundation Web site
HTUhttp://www.opcfoundation.org.
PATENTS
The attention of adopters is directed to the possibility that compliance with or adoption of OPC specifications may require use of an invention covered by patent rights. OPC shall not be responsible for identifying patents for which a license may be required by any OPC specification, or for conducting legal inquiries into the legal validity or scope of those patents that are brought to its attention. OPC specifications are prospective and advisory only. Prospective users are responsible for protecting themselves against liability for infringement of patents.
WARRANTY AND LIABILITY DISCLAIMERS
WHILE THIS PUBLICATION IS BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE, IT IS PROVIDED "AS IS" AND MAY CONTAIN ERRORS OR MISPRINTS. THE OPC FOUDATION MAKES NO WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, WITH REGARD TO THIS PUBLICATION, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO ANY WARRANTY OF TITLE OR OWNERSHIP, IMPLIED WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR WARRANTY OF FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE OR USE. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE OPC FOUNDATION BE LIABLE FOR ERRORS CONTAINED HEREIN OR FOR DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, RELIANCE OR COVER DAMAGES, INCLUDING LOSS OF PROFITS, REVENUE, DATA OR USE, INCURRED BY ANY USER OR ANY THIRD PARTY IN CONNECTION WITH THE FURNISHING, PERFORMANCE, OR USE OF THIS MATERIAL, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
The entire risk as to the quality and performance of software developed using this specification is borne by you.
RESTRICTED RIGHTS LEGEND
This Specification is provided with Restricted Rights. Use, duplication or disclosure by the U.S. government is subject to restrictions as set forth in (a) this Agreement pursuant to DFARs 227.7202-3(a); (b) subparagraph (c)(1)(i) of the Rights in Technical Data and Computer Software clause at DFARs 252.227-7013; or (c) the Commercial Computer Software Restricted Rights clause at FAR 52.227-19 subdivision (c)(1) and (2), as applicable. Contractor / manufacturer are the OPC Foundation, 16101 N. 82nd Street, Suite 3B, Scottsdale, AZ, 85260-1830.
COMPLIANCE
The OPC Foundation shall at all times be the sole entity that may authorize developers, suppliers and sellers of hardware and software to use certification marks, trademarks or other special designations to indicate compliance with these materials. Products developed using this specification may claim compliance or conformance with this specification if and only if the software satisfactorily meets the certification requirements set by the OPC Foundation. Products that do not meet these requirements may claim only that the product was based on this specification and must not claim compliance or conformance with this specification.
Trademarks
Most computer and software brand names have trademarks or registered trademarks. The individual trademarks have not been listed here.
GENERAL PROVISIONS
Should any provision of this Agreement be held to be void, invalid, unenforceable or illegal by a court, the validity and enforceability of the other provisions shall not be affected thereby.
This Agreement shall be governed by and construed under the laws of the State of Minnesota, excluding its choice or law rules.
This Agreement embodies the entire understanding between the parties with respect to, and supersedes any prior understanding or agreement (oral or written) relating to, this specification.
ISSUE REPORTING
The OPC Foundation strives to maintain the highest quality standards for its published specifications; hence they undergo constant review and refinement. Readers are encouraged to report any issues and view any existing errata here: HTUhttp://www.opcfoundation.org/errata.
Revision 1.05.03 Highlights
The following table includes the Mantis issues resolved with this revision.
|
Mantis ID |
Scope |
Summary |
Resolution |
|
|
Clarification |
IEC Requested changes |
Applied requested changes |
|
Clarification |
eCl@sss is now ECLASS |
Changed name throughout. |
OPC Unified Architecture Specification
Part 19: Dictionary Reference
This specification defines an Information Model of the OPC Unified Architecture. The Information Model describes the basic infrastructure to reference from an OPC UA Information Model to external dictionaries like IEC Common Data Dictionary or ECLASS.
The following referenced documents are indispensable for the application of this specification. For dated references, only the edition cited applies. For undated references, the latest edition of the referenced document (including any amendments and errata) applies.
OPC 10000-1, OPC Unified Architecture - Part 1: Overview and Concepts
http://www.opcfoundation.org/UA/Part1/
OPC 10000-3, OPC Unified Architecture - Part 3: Address Space Model
http://www.opcfoundation.org/UA/Part3/
OPC 10000-4, OPC Unified Architecture - Part 4: Services
http://www.opcfoundation.org/UA/Part4/
OPC 10000-5, OPC Unified Architecture - Part 5: Information Model
http://www.opcfoundation.org/UA/Part5/
OPC 10000-8, OPC Unified Architecture - Part 8: Data Access
http://www.opcfoundation.org/UA/Part8/
OPC 10000-100, OPC Unified Architecture - Part 8: Data Access
http://www.opcfoundation.org/UA/Part100/
ISO/IEC 11179-6, Information technology – Metadata registries (MDR) – Part 6: Registration
https://www.iso.org/standard/60342.html
ISO 29002-5, Information automation systems and integration – Exchange of characteristic data – Part 5: Identification scheme
https://www.iso.org/standard/50773.html
ISO/IEC 6523, Information technology – Structure for the identification of organizations and organization parts
https://www.iso.org/standard/25773.html
For the purposes of this document, the terms and definitions given in OPC 10000-1, OPC 10000-3, and OPC 10000-5 apply.
All used terms are italicized in the specification.
This document describes the basic infrastructure an OPC UA Information Model may use to reference external dictionaries like IEC Common Data Dictionary or ECLASS. It defines ObjectTypes, VariableTypes and a ReferenceType and explains how they should be used.
The ObjectTypes are used to represent an external dictionary in an OPC UA AddressSpace. The ReferenceType is used to reference from Nodes in the AddressSpace to the dictionary entries. Such dictionary entries can be seen as external classification or external semantic information.
The type system of OPC UA already provides means to express the semantic of an OPC UA Object. As an example, OPC 10000-100 defines the DeviceType ObjectType expressing that instances of this ObjectType represent devices. Subtypes of the DeviceType are used to add vendor specific semantic. However, the classification and additional semantic of the device in terms of an external data dictionary is not specified further. This document provides means to represent that an Object is for example a differential pressure transmitter in the context of an IEC Common Data Dictionary. This allows clients to automatically retrieve and identify such devices.
This document is an integral part of this standard, that is, the types defined in this document shall be used as defined. However, it is not required but strongly recommended that a Server use the types defined in this document to refer to external dictionaries. The defined types may be subtyped to refine their behaviour.
When a Server references external dictionaries using the types defined in this document, it refers from OPC UA Nodes to dictionary entries. The Server may optionally also provide the hierarchy and content of the external dictionary. Resource consumption needs to be considered, especially in scenarios where the OPC UA Server is part of the firmware of a device.
The types and instances defined in this document are illustrated in Figure 1. The DictionaryEntryType is an abstract base type for dictionary entries. The IrdiDictionaryEntryType and the UriDictionaryEntryType provide concrete types that can be used to represent dictionary entries. The HasDictionaryEntry ReferenceType is used to refer an OPC UA Node to a dictionary entry. The DictionaryFolderType and the Dictionaries Object provide an optional capability to expose the hierarchy of a referenced dictionary.
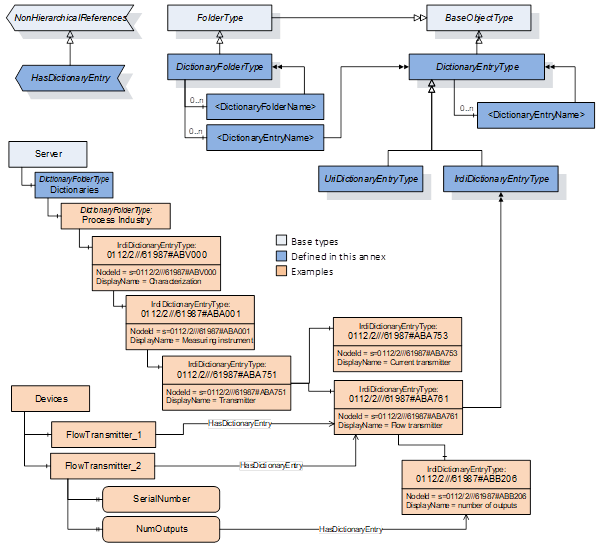
Figure 1 – The dictionary reference types
This abstract ObjectType defines the minimum information needed to identify the data dictionary entry for a respective standard (e.g. IEC Common Data Dictionary). It is formally defined in Table 1.
Concrete dictionary entry types shall inherit from the abstract DictionaryEntryType defining additional Properties and Objects as necessary and specified by the standard body (e.g. further definitions, versioning information etc.).
An instance of such a concrete dictionary entry ObjectType represents an entry in an external data dictionary.
Table 1 – DictionaryEntryType definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||
|
BrowseName |
DictionaryEntryType |
|||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
|||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType / TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
Subtype of the BaseObjectType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
||||
|
HasComponent |
Object |
<DictionaryEntryName> |
DictionaryEntryType |
OptionalPlaceholder |
|
Conformance Units |
||||
|
Address Space Dictionary Entries |
||||
Instances of the DictionaryEntryType can be nested in order to create hierarchies of dictionary entries
This ObjectType provides means to structure dictionary entry Objects. Multiple Objects of the DictionaryFolderType can be nested in order to create hierarchies. The DictionaryFolderType is formally defined in Table 2.
Table 2 – DictionaryFolderType definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
DictionaryFolderType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType / TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
|
Subtype of the FolderType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
|||||
|
HasComponent |
Object |
<DictionaryFolderName> |
DictionaryFolderType |
OptionalPlaceholder |
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
<DictionaryEntryName> |
DictionaryEntryType |
OptionalPlaceholder |
|
|
Address Space Dictionary Entries |
|||||
The IrdiDictionaryEntryType defined in Table 3 is used to represent dictionary entries that use standardized semantic identifiers that conform with International Registration Data Identifiers (IRDI) defined in ISO/IEC 11179-6.
Standardized semantic identifiers are locale independent strings typically specified in international standards like IEC CDD (Common Data Dictionary) (IEC 61987). In order to avoid conflict with various name spaces in these identifiers, the registration authority identifier part of the string used shall be based on ISO 29002-5.
Figure 2 shows the general structure and syntax defined by ISO/IEC 11179-6, ISO 29002-5 and ISO/IEC 6523.
Figure 2 – IRDI overview
Examples for IRDI strings defined by standards using the IRDI format
IEC CDD 0112/2//a/61360_4#AAE867#001 Proximity switch, Output current
ISO 5598 0112-1-a-18582#KAA802#s Pneumatic value
ECLASS 0173/1///#02-8AD792#s Inductive distance sensor, Design of analog output
Table 3 – IrdiDictionaryEntryType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||
|
BrowseName |
IrdiDictionaryEntryType |
|||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType / TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
Subtype of the DictionaryEntryType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
||||
|
Conformance Units |
||||
|
Address Space Dictionary IRDI |
||||
The identifier in the respective external dictionary shall be a unique string. This identifier is used for the NodeId and the BrowseName Attributes of instances of the DictionaryEntryType. The IdentifierType of the NodeId shall be STRING_1 with the identifier from the external dictionary as the value.
The namespace “http://opcfoundation.org/UA/Dictionary/IRDI” shall be used for instance of the IrdiDictionaryEntryType. Subtypes may define different namespaces.
The identifier shall be immutable; meaning that it shall not be reassigned to a different dictionary entry within the scope of the namespace in future versions. Data dictionaries may be publicly defined by standard bodies such as IEC or proprietary (e.g. vendor-specific dictionaries).
The UriDictionaryEntryType defined in Table 4 is used to represent dictionary entries that use URIs as unique identifiers.
Table 4 – UriDictionaryEntryType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||
|
BrowseName |
UriDictionaryEntryType |
|||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType / TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
Subtype of the DictionaryEntryType defined in 5.1. |
||||
|
Conformance Units |
||||
|
Address Space Dictionary URI |
||||
The identifier in the respective external dictionary shall be a unique URI string. This identifier is used for the NodeId and the BrowseName Attributes of instances of the DictionaryEntryType. The IdentifierType of the NodeId shall be STRING_1 with the identifier from the external dictionary as the value.
The namespace “http://opcfoundation.org/UA/Dictionary/URI” shall be used for instance of the UriDictionaryEntryType. Subtypes may define different namespaces.
The identifier shall be immutable; meaning that it shall not be reassigned to a different dictionary entry within the scope of the namespace in future versions. Data dictionaries may be publicly defined by standard bodies such as IEC or proprietary (e.g. vendor-specific dictionaries).
The HasDictionaryEntry ReferenceType is a concrete ReferenceType and can be used directly. It is a subtype of NonHierarchicalReferences.
The Reference to the dictionary entry for any Node is provided by HasDictionaryEntry.
The SourceNode of this ReferenceType can be any Node. The TargetNode of this ReferenceType shall be an Object of DictionaryEntryType or one of its subtypes.
Each Node can be the SourceNode of multiple HasDictionaryEntry References pointing to multiple dictionary entry Objects.
The HasDictionaryEntry ReferenceType is specified in Table 5.
Table 5 – HasDictionaryEntry ReferenceType
|
Attributes |
Value |
||
|
BrowseName |
HasDictionaryEntry |
||
|
InverseName |
DictionaryEntryOf |
||
|
Symmetric |
False |
||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
Comment |
|
Subtype of the NonHierarchicalReferences ReferenceType defined in OPC 10000-3 |
|||
|
Conformance Units |
|||
|
Address Space Dictionary Entries |
|||
The MultiStateDictionaryEntryDiscreteBaseType VariableType is a subtype of the MultiStateValueDiscreteType. It provides dictionary entries for each of the possible states as well as the current state of the MultiStateValueDiscreteType. It is formally defined in Table 6.
Table 6 – MultiStateDictionaryEntryDiscreteBaseType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
MultiStateDictionaryEntryDiscreteBaseType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||||
|
ValueRank |
Scalar |
|||||
|
DataType |
Number |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling |
|
|
Subtype of the MultiStateValueDiscreteType defined in OPC 10000-8 |
||||||
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
EnumDictionaryEntries |
NodeId[][] |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
ValueAsDictionaryEntries |
NodeId[] |
PropertyType |
Optional |
|
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
Data Access MultiStateDictionaryEntryDBT |
||||||
|
Data Access ValueAsDictionaryEntries Property |
||||||
The normal approach of associating DictionaryEntryType Nodes with HasDictionaryEntry References cannot be used with a MultiStateValueDiscreteType VariableType due to the EnumValues Property being an Array, making this Type necessary. References can however be used for other VariableTypes. For example, the TwoStateDiscreteType can use HasDictionaryEntry References with SourceNode being the TrueState and FalseState Properties and TargetNode being the DictionaryEntry Nodes.
EnumDictionaryEntries is a two-dimensional array of NodeIds. The first dimension is used to list all possible dictionary entry values for the related variable in a specific dictionary (e.g. CDD or ECLASS). The second dimension is used to reference this dictionary. The size of the first array dimension shall be the same size as the EnumValues Property.
ValueAsDictionaryEntries provides a list of all dictionary entry values in the different dictionaries related to the current value of the variable. The order of the array entries shall be in the same order used by the EnumDictionaryEntries Property.
If an instance of this type is writeable and the optional ValueAsDictionaryEntries Property is implemented, it shall be writeable as well. Clients writing to the ValueAsDictionaryEntries Property shall use one of the DictionaryEntryType NodeIds defined by the EnumDictionaryEntries Property. This will have the same result as writing the value attribute, but the client does not require knowledge of the values.
The NodeIds represent the dictionary entries and can be generated with dictionary knowledge.
The MultiStateDictionaryEntryDiscreteType VariableType is a subtype of the MultiStateDictionaryEntryDiscreteBaseType. It requires the ValueAsDictionaryEntries Property. It is formally defined in Table 7.
Table 7 – MultiStateDictionaryEntryDiscreteType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
MultiStateDictionaryEntryDiscreteType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||||
|
ValueRank |
Scalar |
|||||
|
DataType |
Number |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling |
|
|
Subtype of the MultiStateDictionaryEntryDiscreteBaseType defined in 7.1 |
||||||
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
ValueAsDictionaryEntries |
NodeId[] |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
Data Access MultiStateDictionaryEntryDBT |
||||||
The Dictionaries Object is used as the browse entry point for dictionaries referenced in the Server. The Object is optional and can be used to expose the hierarchy of the referenced dictionaries or dictionary entries referenced by other Nodes.
The Dictionaries Object is a component of the Server Object defined in OPC 10000-5. The Dictionaries Object references DictionaryEntryType and DictionaryFolderType Object Nodes. It is formally defined in Table 8.
Table 8 – Dictionaries Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
Dictionaries |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
ComponentOf of the Server Object defined in OPC 10000-5. |
|||||
|
HasTypeDefinition |
ObjectType |
DictionaryFolderType |
|
|
|
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
Address Space Dictionary Entries |
|||||
The example in Figure 3 shows how OPC UA Properties of the DeviceType defined in OPC 10000-100 refer dictionary entries in the IEC 61987 Common Data Dictionary.
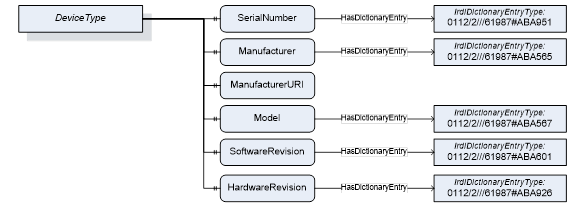
Figure 3 – DeviceType Property example
The example in Figure 4 shows how OPC UA Objects could refer to classes in the IEC 61987 Common Data Dictionary and OPC UA Properties to properties in the data dictionary.
In this example, the weight property is referenced from two OPC UA Properties and the different semantic is provided by the referenced classes Transmitter housing or Transmitter body of the parent OPC UA Objects.
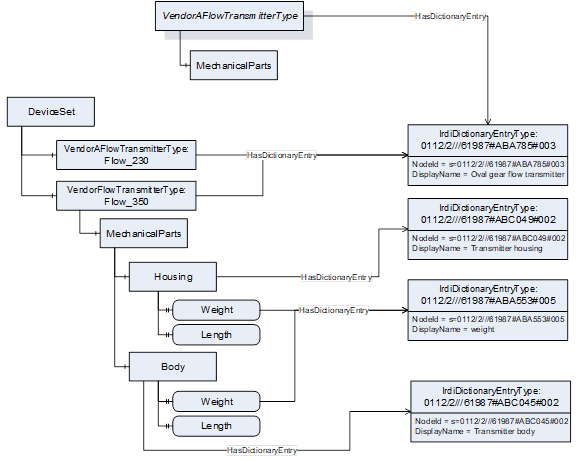
Figure 4 – Example with references to classes and properties
The example in Figure 5 shows how a server can expose the hierarchy of two dictionaries below the optional Dictionaries Object.
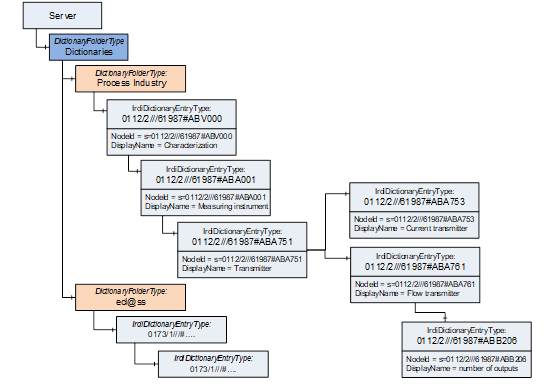
Figure 5 – Example with two dictionaries
__________________